
Planet Aid's annual reports are now published online to help save resources.

Table of Contents:
- Letter from the President
- Results Overview
- Projects
- Planet Aid at Home
- People at Planet Aid
- Financial Statement
Letter from the President
Mobilizing to Fight Textile Waste
Dear Supporters and Friends,
We've had a very busy year fulfilling our mission. Planet Aid’s staff collected approximately 90 million pounds of clothing, shoes, and other textiles from our network of bins and donation centers in 2017.
This success is a product of our efforts to further enhance our partnerships with communities, local governments, and businesses to host our donation bins. These partnerships have made it easier for the public to drop off their unwanted clothing and, in turn, has helped to save valuable resources, relieve landfill burdens, reduce municipal disposal costs, provide good jobs for staff, and—because the useful lives of these resources are extended—help cut down on greenhouse gas emissions.
If you have been following the news, you may have read that the dangers of textile waste have become increasingly serious, and in the past year, organizations and businesses have launched campaigns drawing attention to the problem. One such organization is the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, which published a groundbreaking report called: A New Textiles Economy: Redesigning Fashion's Future.
The report shows that in the last 15 years, clothing production and consumption has doubled. The average consumer purchased 60 percent more clothing in 2014 than in 2000, but the garments are only being used half as long. The result is skyrocketing textile disposal volumes.
I found these statistics to be very alarming, but at the same time I am encouraged that more groups such as the MacArthur Foundation are helping to mobilize support for reversing this trend. Planet Aid has been working for over two decades to divert clothing out of the waste stream, while increasing public awareness about the need to reuse and recycle.
As you know, we are also able to take the textiles we save and convert them into dollars for development, which serves to multiply the impact of every T-shirt, sweater, or pair of slacks we receive. The projects these funds support help people in regions of the world where life is particularly difficult and opportunities are few. On the pages of this annual report you can learn more about our international development projects and also about our domestic initiatives.
We are proud of our accomplishments in 2017, but our success would not have been possible without the generous support of our donors, partners, and staff.

Thank you for making 2017 a great year.
Ester Neltrup, President
2017 in Review


Projects
For the Environment
 In 2017 Planet Aid helped divert more than 90 million pounds of clothing and other textile materials from disposal, thus saving resources for reuse and recycling. Clothing that is disposed of in landfills releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Clothing that is instead reused not only reduces landfill burdens but reduces the need to produce new textile fibers and manufacture new clothing—a resource intensive process requiring large inputs of fossil fuels, water, fertilizer, and pesticides. Reusing clothing thus saves resources and reduces harmful environmental impacts, including reductions in harmful emissions that contribute to climate change.
In 2017 Planet Aid helped divert more than 90 million pounds of clothing and other textile materials from disposal, thus saving resources for reuse and recycling. Clothing that is disposed of in landfills releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Clothing that is instead reused not only reduces landfill burdens but reduces the need to produce new textile fibers and manufacture new clothing—a resource intensive process requiring large inputs of fossil fuels, water, fertilizer, and pesticides. Reusing clothing thus saves resources and reduces harmful environmental impacts, including reductions in harmful emissions that contribute to climate change.
Read more about our recycling efforts.
For People
For more than two decades, Planet Aid has been supporting development projects across the globe helping to fight poverty. Through the funds generated by collecting and selling used clothing and by receiving support from public and private donors, Planet Aid has been able to provide life-changing, sustainable assistance to those in need. Below is an overview of the projects we supported in 2017.
Locations of Development Projects
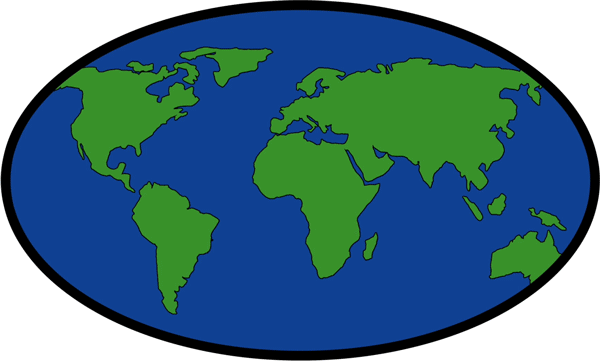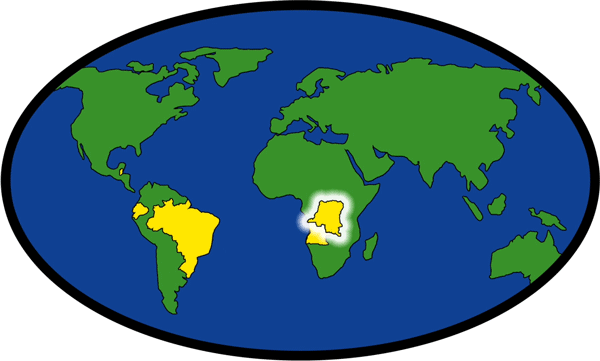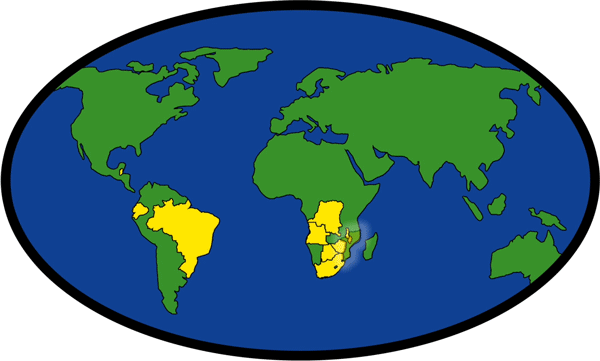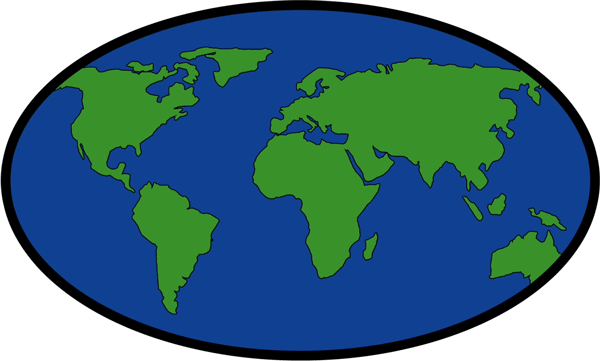
| Angola | Democratic Republic of the Congo | Malawi |
| Belize | Ecuador | Mozambique |
| Botswana | Laos | South Africa |
| Brazil | India | Zimbabwe |
Types of Projects We Support
Food and Nutrition • Education • Community Development
Health • Sustainable Agriculture
Food and Nutrition
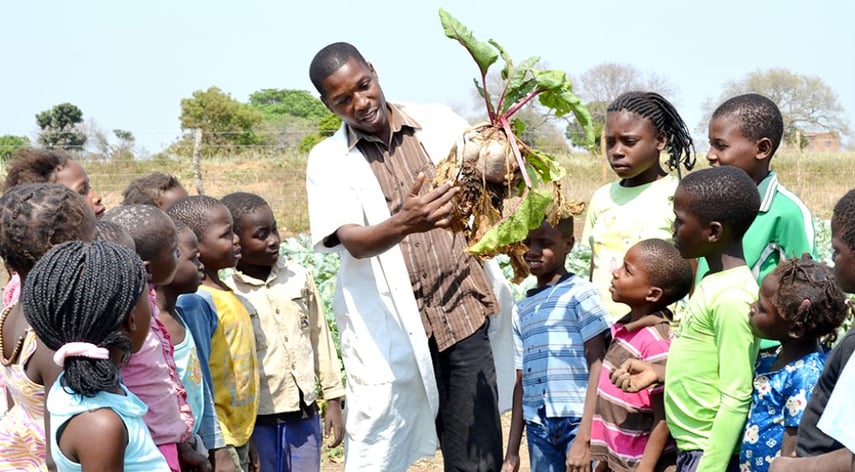

Nutrition Projects
Countries: Malawi, Mozambique
 Malnutrition in children and pregnant women is often a problem within developing countries, leading to a high level of child mortality. The nutrition projects supported by Planet Aid in Malawi and Mozambique seek to reduce malnutrition by improving nutrition knowledge and practices within target communities.
Malnutrition in children and pregnant women is often a problem within developing countries, leading to a high level of child mortality. The nutrition projects supported by Planet Aid in Malawi and Mozambique seek to reduce malnutrition by improving nutrition knowledge and practices within target communities.
The projects reduce malnutrition as the residents gain knowledge on the importance of eating diverse foods, learn to garden for themselves, and improve their cooking practices and processes. By introducing a diversity of fruits and vegetables and empowering residents to grow their own food, these nutrition projects have seen a definitive drop in the number of malnourished residents.
In 2017, the projects planted more than 47,000 fruit trees and established hundreds of gardens.
Food for Knowledge Project
Countries: Mozambique
 The Food for Knowledge Project (FFK) is Planet Aid’s comprehensive school lunch and education initiative. The project is funded by the U.S. Department of Agriculture as part of the McGovern-Dole International Food for Education and Child Nutrition Program.
The Food for Knowledge Project (FFK) is Planet Aid’s comprehensive school lunch and education initiative. The project is funded by the U.S. Department of Agriculture as part of the McGovern-Dole International Food for Education and Child Nutrition Program.
In addition to providing daily meals for students, the project trains primary school teachers; establishes school gardens and small-scale farms; facilitates after-school learning clubs; builds literacy skills; provides nutrition education; and helps construct and refurbish school kitchens, wells, and latrines.
The Literacy Component of FFK was fully operational in 2017, helping children learn to read and write in their local languages. FFK, in partnership with Cambridge Education, developed early grade reading materials in two local languages used by the children at home. This has helped to remove a key obstacle of having to first learn to read in Portuguese (the language traditionally used in schools and less familiar to most students). Additionally, more than 9,000 children received textbooks and other teaching and learning materials in their native language that were developed by the project.
In 2017, FFK also continued to serve a hot lunch to 82,000 children, and trained more than 1,500 teachers.
Read more about the Food for Knowledge Project.
Education
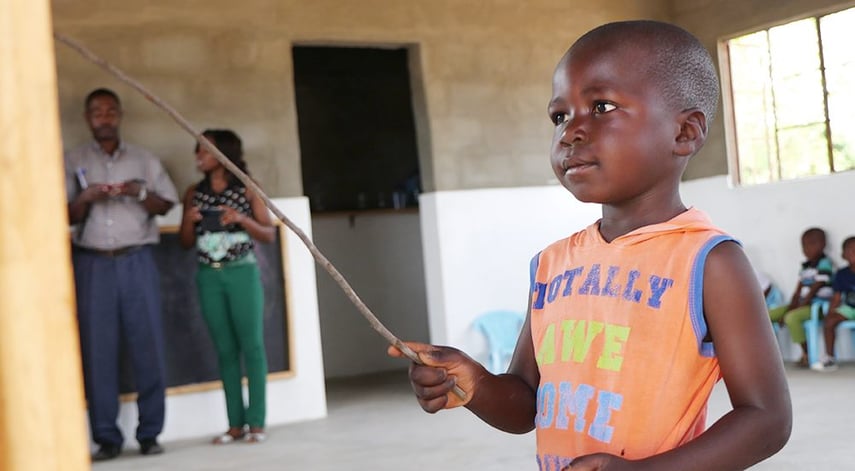

Teacher Training Projects
Countries: Angola, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, India, Mozambique
 Developing countries often suffer a dearth of qualified and skilled teachers for primary schools. Those teachers who do exist are working with large classes—often more than 60 students at once. This situation puts dedicated and resourceful teachers in high demand.
Developing countries often suffer a dearth of qualified and skilled teachers for primary schools. Those teachers who do exist are working with large classes—often more than 60 students at once. This situation puts dedicated and resourceful teachers in high demand.
Planet Aid supports teacher-training colleges that prepare and equip future teachers with a comprehensive set of tools to enable them to be change agents in the classrooms and communities they will serve. Along with technical knowledge and training in mathematics, reading, writing, and other subjects, these teachers are prepared to create exciting learning environments and encourage students (many of whom face pressure to drop out) to stay in school. In 2017, approximately 5,000 teachers were trained at the colleges.
 The teaching practice is not only valuable for the soon-to-be teachers, but also for the communities. For example: three schools near the teacher-training college in Kunene, Angola would not have been able to be in operation (due to a lack of full-time teachers) if it weren’t for the student teachers. Their presence in the village allowed over 100 children to continue their education in 2017.The teachers in training focus on the pedagogical aspects of teaching; learn important background information about the schools, communities, and students; visit various areas of the country to see where teachers are most needed; and practice teaching at primary schools.
The teaching practice is not only valuable for the soon-to-be teachers, but also for the communities. For example: three schools near the teacher-training college in Kunene, Angola would not have been able to be in operation (due to a lack of full-time teachers) if it weren’t for the student teachers. Their presence in the village allowed over 100 children to continue their education in 2017.The teachers in training focus on the pedagogical aspects of teaching; learn important background information about the schools, communities, and students; visit various areas of the country to see where teachers are most needed; and practice teaching at primary schools.
The teachers trained through Planet Aid–supported teacher-training colleges also learn how to mobilize, strengthen, and encourage community development, expanding their reach beyond the children in the classroom to families, villages, and larger communities. These community outreach projects vary from a focus on women’s empowerment and sanitation, to nutrition and environmental protection.
Read more about Teacher Training.
Kadam Step-Up Center
Countries: India
 The focus of the Kadam Step-Up Centers is to provide children who have never attended school, or who have dropped out, with “bridge education” so they can transition into regular public education. There is a large number of migrant families in India where the centers operate, and many of those children haven’t had the opportunity for education due to a lack of funding, a lack of legal documents, and many other factors.
The focus of the Kadam Step-Up Centers is to provide children who have never attended school, or who have dropped out, with “bridge education” so they can transition into regular public education. There is a large number of migrant families in India where the centers operate, and many of those children haven’t had the opportunity for education due to a lack of funding, a lack of legal documents, and many other factors.
The Step-Up Center’s curriculum covers mathematics, science, English, and computer training, along with other subject requirements established by the Government of India. In 2017, Planet Aid supported 318 Step-Up Centers and helped over 12,000 out-of-school children, and approximately 5,000 of which were transitioned to mainstream schools throughout the year.
Read more about Kadam Step-Up Centers.
Early Education Initiatives
Countries: Mozambique, South Africa
 Planet Aid-supported preschool initiatives provide access to early childhood education, a key to ensuring proper development and academic success. These community-based preschools not only teach young children the basics of learning, but also seek to increase the involvement of parents and guardians in their children’s day-to-day lives and their education.
Planet Aid-supported preschool initiatives provide access to early childhood education, a key to ensuring proper development and academic success. These community-based preschools not only teach young children the basics of learning, but also seek to increase the involvement of parents and guardians in their children’s day-to-day lives and their education.
Preschools are often not part of the formal education process for children in developing countries, but it is important to their cognitive development to be stimulated and given problem-solving challenges. The aim of these projects is to establish a sustainable model for integrating preschools into the formal education system, giving more children a better foundation for later learning.
In 2017, the early education initiatives supported by Planet Aid reached nearly 4,000 preschool children and their parents, trained 500 local leaders on the importance of preschool education, and built 44 preschools in Mozambique.
Read more about Early Education Initiatives.
Nikhalamo Girls Stay in School Project
Countries: Mozambique
 Nikhalamo in the local Chuabo language means “I am here to stay.” This name affirms the project’s aim to reduce obstacles for girls transitioning from primary school to secondary school to ensure that they stay in school.
Nikhalamo in the local Chuabo language means “I am here to stay.” This name affirms the project’s aim to reduce obstacles for girls transitioning from primary school to secondary school to ensure that they stay in school.
The project has three main goals: first, to improve girls’ school retention and performance rates; second, to transform learning environments through improving water and sanitation, and promoting gender equality; and third, to build a community-led support system for the girls, which includes mentoring in life skills and moral support. The project worked with more than 1,300 vulnerable girls and conducted 270 door-to-door community campaigns to raise awareness about the importance of girls’ education.
Read more about the Nikhalamo Girls Stay in School Project.
School Improvement Program
Countries: India
 The School Improvement Program aims to promote the learning of girls in schools by identifying the core obstacles that adversely affect their education and putting components in place to help alleviate those obstacles. Mainly, the project provides academic support through implementation of support centers that provide after-school academic guidance, group study sessions, and interactive activities in all subjects. The School Improvement Project not only improves academic success, but also encourages good communication, presentation, and creative skills.
The School Improvement Program aims to promote the learning of girls in schools by identifying the core obstacles that adversely affect their education and putting components in place to help alleviate those obstacles. Mainly, the project provides academic support through implementation of support centers that provide after-school academic guidance, group study sessions, and interactive activities in all subjects. The School Improvement Project not only improves academic success, but also encourages good communication, presentation, and creative skills.
In 2017, the School Improvement Project in Tamil Nadu, India added seven new schools and ended the year serving 8,000 young girls through 253 support centers. The project worked with 93 government schools, and conducted 540 co-curricular and cultural activities.
Ponesai Vanhu Junior School
Countries: Zimbabwe
 The Ponesai Vanhu Junior School provides shelter, education, and support for orphaned and vulnerable children (age 18 and under) who would have been abandoned, abused, or destitute. The children are able to live in a supportive environment that helps to rehabilitate them with an education and social development.
The Ponesai Vanhu Junior School provides shelter, education, and support for orphaned and vulnerable children (age 18 and under) who would have been abandoned, abused, or destitute. The children are able to live in a supportive environment that helps to rehabilitate them with an education and social development.
The school focuses on providing good education in gender equality, diet and nutrition, and technology and computer studies. The students do most of their learning via tablets and desktop computers, and in 2017, the school provided 15 tablets and training to 38 teachers at the nearby Chindunduma Primary School. This allowed the primary school to help better educate 800 children.
Ponesai, supported by Planet Aid, provides the basics for a stable and healthy life with food and nutrition, clothing, medical attention, and psychological support. During 2017, the school housed 56 children, two of whom were reunited with their families during the year.
Read more about the Ponesai Vanhu Junior School.
Vocational and Skills Training
Countries: Angola, Zimbabwe
 Planet Aid supports four vocational and skills training schools, which enroll men and women, aged 12 to 20, to increase employability and opportunities for entrepreneurship. In 2017, these schools trained 550 young people.
Planet Aid supports four vocational and skills training schools, which enroll men and women, aged 12 to 20, to increase employability and opportunities for entrepreneurship. In 2017, these schools trained 550 young people.
Courses at the schools expand on the foundational knowledge of mathematics, reading and writing, biology, chemistry, and other subjects. Students may also study in particular vocational areas such as business, clothing design, mechanics, masonry, catering, and horticulture. Students are also instilled with knowledge on economics and commerce to empower entrepreneurial thinking.
During their training, students often acquire apprenticeships or gain hands-on experience in other ways. For example, the masonry students at the Ponesai Vanhu Technical College in Zimbabwe won a construction bid for the Chemhondoro Secondary School. They began construction on two classrooms, two teachers’ houses, and two latrine blocks in February of 2017 and completed construction in November.
Read more about vocational and skills training.
Frontline Institute
Countries: Zimbabwe
 Frontline Institute trains individuals in development, helping create a dedicated cadre of development professionals working to alleviate dehumanizing circumstance around the globe. Located in Zimbabwe, students at Frontline gain a unique and international view of the challenges of development and the tools to make development efforts more effective.
Frontline Institute trains individuals in development, helping create a dedicated cadre of development professionals working to alleviate dehumanizing circumstance around the globe. Located in Zimbabwe, students at Frontline gain a unique and international view of the challenges of development and the tools to make development efforts more effective.
Most Frontline students are from countries where Planet Aid supports projects and will often take the knowledge gained back to their home countries and communities to further the efforts of development teams already in place. So far, Frontline has trained more than 4,500 students, most of whom are still working within the Humana People to People Federation (of which Planet Aid is a member).
Frontline trains activists to be on the frontlines of development and to pave the way for the expansion of projects and fields. Frontline trains students to become political and cultural persons who act when they observe injustice and are passionate about creating development together with people in rural communities.
In 2017, Frontline trained 112 students who produced enough organic livestock and crops to make the school self-sustaining, planted more that 400,000 trees, installed 38 handwashing facilities in the surrounding communities, and connected with over 400 households to educate them on the symptoms, severity, and prevention of Malaria.
Community Development
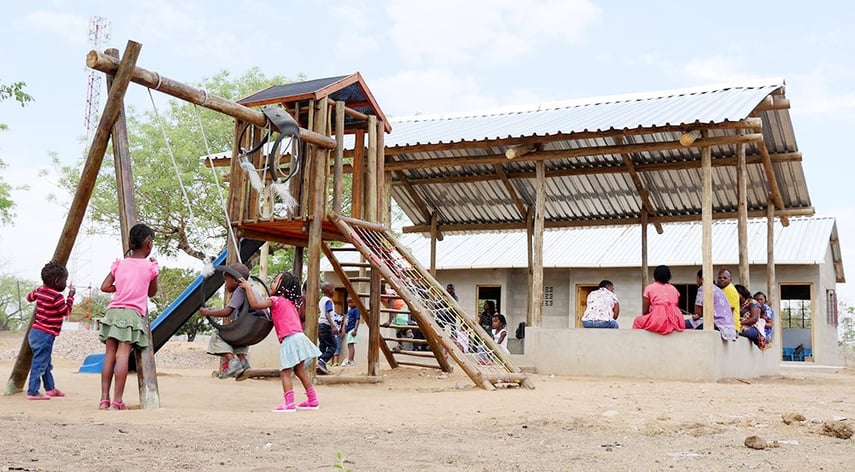

Child Aid Projects
Countries: Belize, Botswana, Brazil, Ecuador, Laos, South Africa, Zimbabwe
 Child Aid projects are community-based initiatives that use a holistic approach to mobilize residents into organizing themselves and attacking community problems. The goal is to improve their living conditions and ensuring a sound upbringing for their children.
Child Aid projects are community-based initiatives that use a holistic approach to mobilize residents into organizing themselves and attacking community problems. The goal is to improve their living conditions and ensuring a sound upbringing for their children.
The projects empower communities with essential skills in the areas of health, water and sanitation, education, agriculture and food security, income generation, environmental awareness, and childhood development opportunities. The aim is to improve the conditions of households and communities where the children live.
While the goals of all Child Aid projects are the same, the implementation varies greatly between each project location. The projects seek to address specific problems within each community and serve as a tool in expanding the capacity of the residents to solve their own problems.
In 2017, Child Aid projects supported by Planet Aid established 3,200 gardens, which helped insure proper nutrition for 2,000 orphans; vaccinated more than 3,000 children; ensured a preschool education for 8,500 children; and distributed more than 100,000 condoms.
Health

Community-Based Diabetes Detection and Care Project
Countries: India
 Awareness is a key component in ensuring better treatment and control of diabetes, a disease with growing prevalence in India. To create more knowledge around diabetes and promote healthy lifestyles, Planet Aid supported the Community-Based Diabetes Detection and Care Project in 2017.
Awareness is a key component in ensuring better treatment and control of diabetes, a disease with growing prevalence in India. To create more knowledge around diabetes and promote healthy lifestyles, Planet Aid supported the Community-Based Diabetes Detection and Care Project in 2017.
This project takes to the streets, testing community members for diabetes, spreading knowledge about the disease, and ensuring proper and continued care for those diagnosed. The participants are partnered with others so that they can encourage each other and motivate their neighbors in continuing treatment. This helps develop a favorable environment within the community to prevent diabetes.
This project reached out to nearly 80,000 people, encouraging them to be tested for diabetes, testing over 14,000 of them, and then establishing a treatment plan for 1,000. The project also trained 44,000 students and community leaders in prevention techniques.
Total Control of the Epidemic
Countries: Malawi, South Africa
 Total Control of the Epidemic (TCE) is the model Planet Aid–supported projects use to help communities take control of the HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis (TB) epidemics that plague their families.
Total Control of the Epidemic (TCE) is the model Planet Aid–supported projects use to help communities take control of the HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis (TB) epidemics that plague their families.
TCE projects play an important role in capacity development and knowledge sharing by facilitating links between health services and the communities, and by introducing innovative approaches for wide-scale reach and buy-in of services. The main activity in TCE is door-to-door campaigning to provide HIV/AIDS and TB testing in the comfort of the person’s home, and then connecting HIV positive individuals with treatment facilities. This also allows the facilitators to explain the spread and impact of sexually transmitted infections and non-communicable diseases.
TCE projects supported by Planet Aid reached out to over 200,000 people and distributed 48,000 condoms in 2017.
HOPE
Countries: Botswana, South Africa
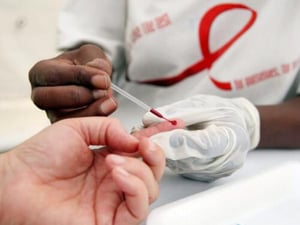 HOPE is a people-to-people intervention model that reduces the spread of HIV/AIDS and TB, and offers care and support to affected people. The aim is to give hope to participants, encouraging them to see that they can overcome the epidemics and look towards a future free of HIV/AIDS and TB.
HOPE is a people-to-people intervention model that reduces the spread of HIV/AIDS and TB, and offers care and support to affected people. The aim is to give hope to participants, encouraging them to see that they can overcome the epidemics and look towards a future free of HIV/AIDS and TB.
To do this, HOPE uses a community-based, bottom-up approach where the community is engaged and encouraged to become the agents of change and to prevent new infections in their communities.
Hope provides HIV/AIDS and TB in-home testing, referral for treatment, condom distribution, support groups, psychological support, awareness education in schools, and establishes food gardens and nutrition centers.
HOPE projects also host community meetings to inform residents on the importance of behavioral change in relation to spreading HIV/AIDS and TB. Some topics covered at these meetings are: improving gender relations; encouraging and enabling support for orphans and other venerable children; fighting stigma associated with HIV/AIDS; preventing mother-to-child transmission; the importance of family planning and strategies to achieve it; the necessity for treatment adherence; and the benefits of male medical circumcision.
In 2017, the 10 Planet Aid-supported HOPE projects connected with 240,000 people, testing 40,000 for HIV/AIDS and/or TB, and distributed 6.6 million condoms.
Sustainable Agriculture

Farmers' Clubs
Countries: Belize, Brazil, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ecuador, Zimbabwe
 Planet Aid supports small-scale farmers through Farmers’ Clubs, which help to improve the livelihoods of rural farmers through conservation farming. The farmers in one project area are broken into groups (or “clubs”) and work together to learn and improve their farming techniques.
Planet Aid supports small-scale farmers through Farmers’ Clubs, which help to improve the livelihoods of rural farmers through conservation farming. The farmers in one project area are broken into groups (or “clubs”) and work together to learn and improve their farming techniques.
The farmers are trained to mitigate and adapt to climate change, becoming more resilient in their changing environments. The clubs receive agricultural training in topics like crop and environmental management, vegetable production, and crop diversification. The projects also provide technical assistance and facilitate visits among farmers so that they can share experiences on sustainable farming and low-cost solutions.
In 2017, Planet Aid-supported Farmers’ Clubs involved more than 18,000 farmers and helped plant more than 73,000 trees.
Read more about Farmers' Clubs.
Fishers’ Clubs
Country: Brazil
 Similar to the Farmers’ Club, the Fishers’ Clubs in Bahia Pesca, Brazil, seek to improve the sustainable management of natural resources and empower local fishermen and women to diversify their diets, increase their food security, productively market their product, and be a part of social decisions and organization.
Similar to the Farmers’ Club, the Fishers’ Clubs in Bahia Pesca, Brazil, seek to improve the sustainable management of natural resources and empower local fishermen and women to diversify their diets, increase their food security, productively market their product, and be a part of social decisions and organization.
This project, supported by Planet Aid in 2017, served 1,250 fishing families and saw a reduction of poverty and an increase in the participants’ belief in their own capacity. More citizens are actively participating in their communities to further progress on the key issues of health, food production, education, and social welfare. The fishermen and women in the project connected with another 2,250 fishing families in the area to share their knowledge. The Fishers’ Clubs in Brazil are also supporting women’s empowerment. Two-thirds of the participants in the clubs are women, with many taking on leadership roles within the clubs.
Distribution of Support by Sector
| Distribution of Support by Sector | Dollar Amount |
|---|---|
| Nutrition Programs | 27 |
| Health & HIV/AIDS | 1 |
| Sustainable Agriculture | 2 |
| Preschool & Primary Education | 29 |
| Training of Primary School Teachers | 25 |
| Other Education & Training | 6 |
| Community Development | 3 |
| Domestic Charity Support | 4 |
| In-kind Support | 3 |
Planet Aid at Home
By making it more convenient for consumers to drop off their unwanted clothing, Planet Aid helps increase textile reuse and recycling rates thereby reducing environmental impacts associated with the manufacture and disposal of textile products. In 2017 Planet Aid collected and recycled nearly 90 million pounds of clothes and shoes in the United States.
Here are a few other highlights from our work in 2017.
Planet Aid Installs Large Solar Array
 Planet Aid unveiled a 70,000 square foot rooftop solar power–generating installation at the Milford, Massachusetts facility in September of 2017. The array is one of the largest roof-mounted solar arrays in the state, and the solar panels will generate nearly 700,000 kW per year. This renewable source will save approximately 28,000 barrels of oil from being burned, and help to reduce CO2 emissions into the atmosphere by 12,000 metric tons, which is equivalent to saving over 1.3 million gallons of gasoline or planting more than 11,000 acres of new forest. The array will also contribute to Massachusetts' goal of lowering greenhouse gas emissions to 15% of 1990 levels by 2020. Read more
Planet Aid unveiled a 70,000 square foot rooftop solar power–generating installation at the Milford, Massachusetts facility in September of 2017. The array is one of the largest roof-mounted solar arrays in the state, and the solar panels will generate nearly 700,000 kW per year. This renewable source will save approximately 28,000 barrels of oil from being burned, and help to reduce CO2 emissions into the atmosphere by 12,000 metric tons, which is equivalent to saving over 1.3 million gallons of gasoline or planting more than 11,000 acres of new forest. The array will also contribute to Massachusetts' goal of lowering greenhouse gas emissions to 15% of 1990 levels by 2020. Read more
Planet Aid Goes Across the Bay
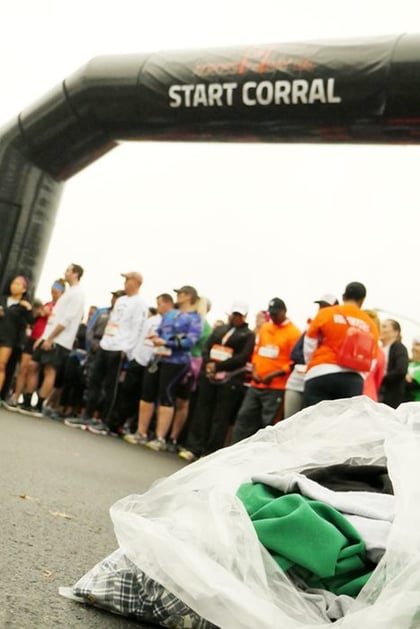

Each November thousands of runners cross the Chesapeake Bay Bridge in Annapolis, Maryland as part of the Across the Bay 10k. And each November, Planet Aid is there to pick up any dropped clothing along the route. Many runners remove and drop layers as they go along the course to stay cool. Instead of letting the clothing end up in a landfill, Planet Aid volunteers are there to collect any articles shed during the race.
This is one of many community events that Planet Aid is a part of each year. We also sponsor clothing and shoe drives in all states served by Planet Aid to encourage textile recycling.
Planet Aid Partners with the Ohio Department of Rehabilitation and Correction
About three years ago, Planet Aid first partnered with the Ohio Department of Rehabilitation and Correction and the Go Home to Stay Home program, and hit a milestone in April of 2017 when the State gave approval to add a community service component to the partnership.
The program helps provide shoes, clothing, food vouchers, furniture vouchers, and more to inmates being released; and thanks to the new approval, now inmates are able to repaint and relabel weathered collection bins during their sentence to earn community service hours and reduce their fines. Read more
Planet Aid Provides Coats in Rochester to Hurricane Victims

In November of 2017, Planet Aid teamed up with Rochester, New York's Ibero-American Action League to provide more than 1,000 coats to those in need. The area had recently received an influx of Puerto Rican refugees, who fled their island after the devastation of Hurricane Maria. Prior to Maria, Rochester already had one of the largest Puerto Rican communities in the continental United States.
Planet Aid has an operations center in Rochester, and has been long been serving the greater Rochester and Syracuse communities.
Planet Aid Thrift Center Celebrates Second Anniversary

In October of 2017, the Planet Aid Thrift Center celebrated its second anniversary. Customers were asked to share what they love about the store:
“I’m here at least once a week, looking for new clothes—brand names and great prices.”
“You find something all the time, you don’t have to spend a lot of money, and it’s for a good cause.”
“The cleanliness is amazing!”
“It’s large and the people are very generous.”
“You can really make out pretty good with a 20-dollar bill!”
Hear more customer comments
People at Planet Aid
Board and Officers

Staff Snapshots...
 José Delgado is the operations manager for Planet Aid in Rochester, New York. José started with Planet Aid in June of 2013, and originally applied as a driver. Due to his previous experience in management, he was hired as the transportation manager and then took over as operations manager.
José Delgado is the operations manager for Planet Aid in Rochester, New York. José started with Planet Aid in June of 2013, and originally applied as a driver. Due to his previous experience in management, he was hired as the transportation manager and then took over as operations manager.
Community is the number one priority for José and he brings this passion into his work. “I love what Planet Aid does,” he said. “Traveling around my community and meeting local business owners is my favorite part of the job.”
José and his family are deeply and personally connected with the growing Puerto Rican community in Rochester. He, along with his wife Angelica, were instrumental in creating Planet Aid’s partnership with IBERO and are key in hosting the annual coat giveaway each year. “I am so appreciative that Planet Aid provides me the opportunity to coordinate this,” José said. “It allows me to give back to my own community.”

Pamela Pine is a Partnership Specialist at Planet Aid, focused on reaching out to and cultivating relationships with corporate and foundation donors. Working out of the Elkridge, Maryland office, Pamela identifies the countries and programs that mesh well with a specific donor’s focus, and then strategizes with Planet Aid and country staff to see the project funding to fruition.
Pamela has a PhD in international public health communication and two master’s degrees, one in international affairs and the other in public health, stacked on top of her 40 years of global development experience. She spent close to a decade in her early career working overseas, then continued her work in international health and development from the United States.
When she’s not traveling, she’ll be found networking or writing up proposals for continued funding. “I like to be productive. To think. To strategize. To have an impact,” she said. “But it’s the people and outcomes for them that have always been the draw for me.”
Pamela started with Planet Aid in 2015 upon “understanding more about Planet Aid’s approach to development: building capacity in people and communities to drive change,” she said. “I would never have a job that wouldn’t have an impact on people’s lives—that didn’t better people’s lives. That’s just how I’m built. The work Planet Aid does and my contribution to the end goals are important to the world and important to me.”

Louise Godek started with Planet Aid over ten years ago in 2007. She has a history in accounting and works as the accounts receivable clerk at the Planet Aid corporate office in Milford, Massachusetts. She ensures that all the shipments made to buyers are properly aggregated and accounted for, working closely with a broker.
During her tenure with the company, Louise has had the opportunity to see the immense growth of Planet Aid. “When I started, the office was tiny and attached to a small warehouse. We’ve definitely grown as a company and that’s mirrored through the Milford office.”
In 2013, Planet Aid opened its newly renovated Milford warehouse; and in September of 2017, the solar array atop the Milford warehouse went live.
Louise recently received her 10-year service award, one of her fondest memories of her time with Planet Aid. She said that she’s stayed with the organization for many reasons: “The work itself is enjoyable, I get along well with coworkers, and I like my supervisors. If I have an idea, I can bring it to them to see about implementation. It’s casual and open. Can I just say that I love it here?”
Financial Statement
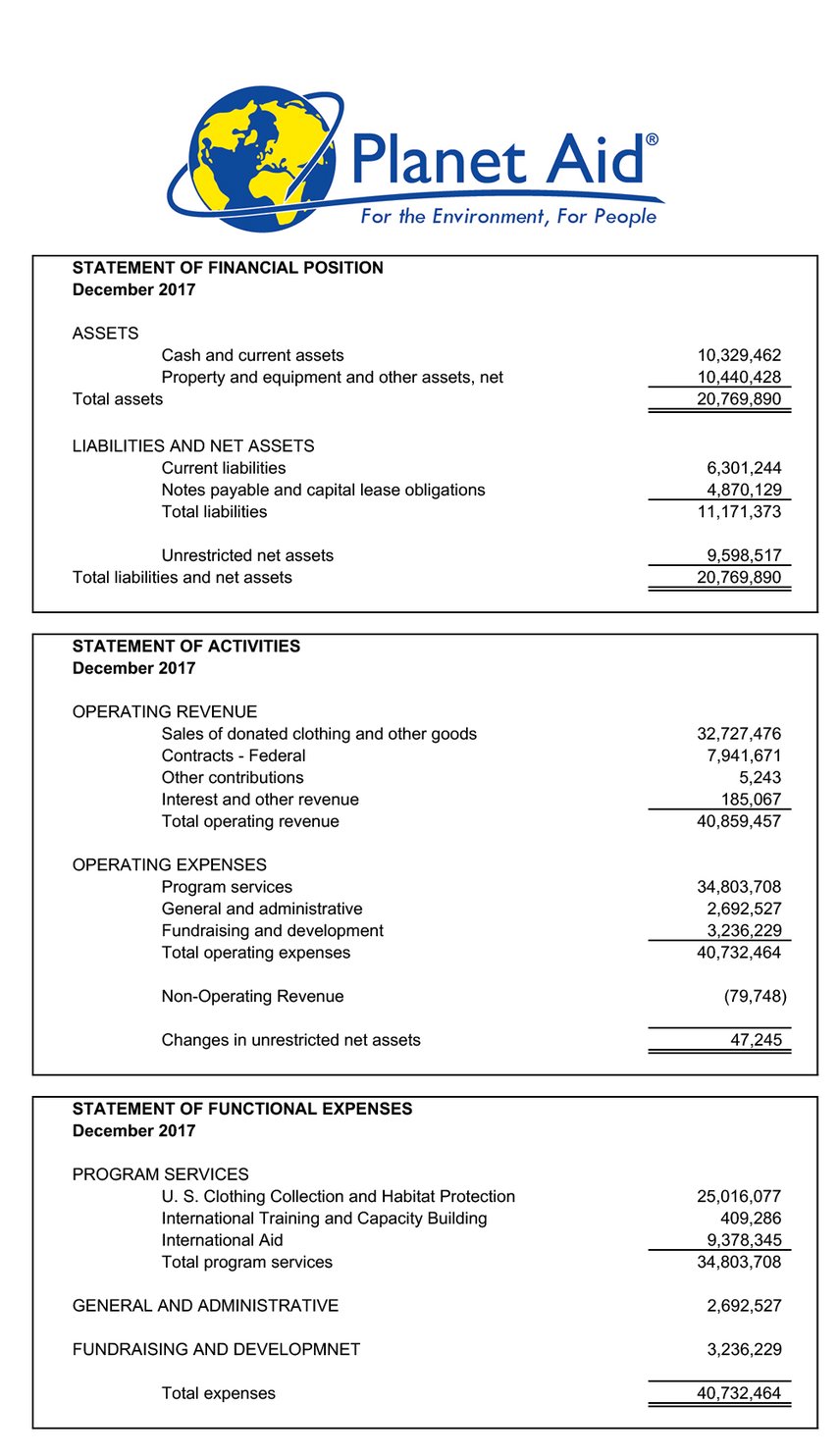
Allocation of Funds
| Task | Internal Program Support |
|---|---|
| Program Services | 85 |
| General and Administrative | 7 |
| Fundraising and Development | 8 |
